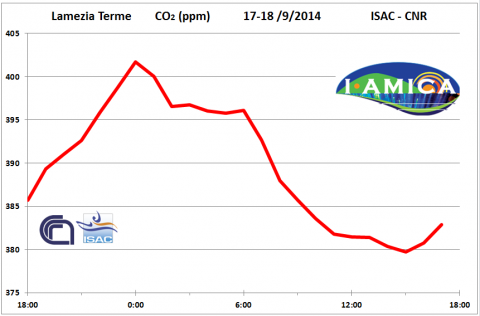
Greenhouse gas measurements started at Lamezia Terme, Lecce and Mt. Curcio: first measurements of CO2, CO, CH4 and WV
j F Y in Notizie
On 2014 September 17, in the framework of the PON I-AMICA Project, new continuous greenhouse gas measurements have been started at the ISAC-CNR Observatories in Lamezia Terme and Lecce (November 4th) and at the IIA-CNR Observatory of Mt. Curcio by using a CRDS system.
PICARRO G2401, is based on the Cavity-Ring-Down Spectroscopy (CRDS) technology that enables an effective measurement path length of up to 20 kilometers in a compact cavity, which results in exceptional precision and sensitivity for simultaneous CO2, CO, CH4 and H2O measurements. This instrument represents one of the most advanced standards recognized by the World Meteorological Organization for the monitoring of greenhouse gas atmospheric concentrations.
CO2 and CH4, are the most important greenhouse gases directly affected by human activities, while CO is a key-compound in many chemical reactions occurring within the troposphere (e.g. the photo-chemical production of ozone) and it also represents an effective tracers for combustion emissions. Water vapor (H2O) is the most important greenhouse gas existing within the Earth’s atmosphere. Its precise detection by the CRDS technique, allows an automated and integrated assessment of its influence on the CO2, CH4 and CO measurements.